The empathy revolution: How LMM models are transforming patient service standards
The empathy revolution: How LMM models are transforming patient service standards
Over the past decade, automation in healthcare has been associated by patients mainly with rigid IVR messages and the need to select numeric options on a phone keypad. However, 2026 marks a fundamental shift. With the implementation of next-generation language models—LMMs (Large Multimodal Models)—the boundary between a conversation with a human and an interaction with a machine is becoming blurred. It is no longer just about efficiently booking an appointment, but about how the patient feels during that conversation. We are entering an era of digital empathy that will permanently reshape the face of medical facilities.
In brief: Key takeaways from the article
- LMM models introduce a new level of quality in healthcare by offering fluent, natural conversations that go beyond simple “question–answer” patterns.
- Machine empathy enables AI systems to analyze a patient’s tone of voice and emotions, allowing the bot’s responses to be adjusted to the caller’s psychological state.
- Voicebot 2.0 technology eliminates irritating delays and interpretation errors, making seniors and stressed individuals feel better understood.
- Security and ethics remain foundational—advanced models are designed to support patients while maintaining rigorous medical data protection standards.
- Synergy with staff enables the transfer of patients who require the most support to live consultants, with full contextual information about their issue.
A new era of communication: From decision trees to open dialogue
Traditional automated service systems were based on so-called decision trees. If a patient did not utter a specific keyword, the system became confused, forcing repetitions and building frustration. By using AI voicebots based on LMM architecture, this model is being abandoned.
Multimodal models are able to process information not only as text but also understand context, pauses, and even hesitation in a voice. LMM technology is a true “game changer” in today’s voice communication. For a modern virtual consultant, a conversation with a patient becomes a dynamic process. The patient can interrupt the bot, ask follow-up questions while providing information, or change the topic, and the system will smoothly adapt to these changes. This flexibility is what builds the feeling of “being heard.”
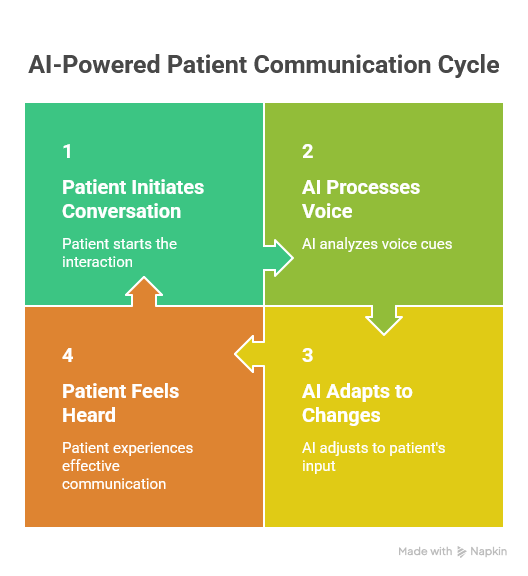
Digital empathy in medical practice
In medicine, empathy is not an add-on—it is a diagnostic and therapeutic tool. A patient calling a clinic is often under stress, experiencing pain, or feeling anxiety. A traditional automated system responding with dry messages only intensifies this stress.
Modern next-generation medical voicebots are trained on vast datasets that include not only medical knowledge but also principles of interpersonal communication. The system can recognize when a patient is agitated and automatically adjust its voice tone to be more calming or use phrases that express understanding (e.g., “I understand that this is a difficult situation for you; I will check the earliest available appointment right away”). Such a communication strategy makes the facility perceived as friendly and patient-centered.
Table: Comparison of patient service system generations
| Feature | Voicebot 1.0 (Script-based) | Voicebot 2.0 (LMM Models) | Impact on patient experience (PX) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conversation style | Rigid commands and keywords | Natural dialogue, full sentences | Reduced stress and frustration |
| Response to interruption | System continues speaking (no reaction) | Immediate stop and listening | Sense of control over the conversation |
| Intent understanding | Only simple inquiries | Complex issues and multi-threaded conversations | More effective issue resolution |
| Emotion analysis | None | Recognition of tone and mood | Feeling understood (empathy) |
| HIS integration | Often limited | Full, two-way, real-time integration | Shorter handling time and data confidence |
Data security in the era of generative AI
The introduction of advanced LMM models raises questions about privacy. At EasyCall, we take an uncompromising approach. Data security in LMM-based voicebots is ensured through local data processing in secure operational centers within the EU.
Unlike publicly available AI models, medical systems operate in “closed loops.” Information about a patient’s health condition is not used to train global algorithms but is used solely to handle a specific request and to feed the facility’s HIS system. This guarantees compliance with GDPR and the strict e-health standards in force in 2026.
Case study: When technology meets human need
An excellent example of system evolution is the reduction in missed calls at a hospital in Kraków. Although that implementation achieved operational success, the introduction of LMM models makes it possible to go one step further. The virtual receptionist not only answers 100% of calls but does so in a way that builds patient loyalty.
For oncology or cardiology patients, where every piece of information is invaluable, response speed and the quality of information provided over the phone are critical. Our experience with call centers for private hospitals shows that patients who are handled efficiently and politely by AI are less likely to cancel appointments and more likely to recommend the facility to others.

Porozmawiaj z naszym specjalistą
Summary: The future of medicine has a human voice
The empathy revolution in healthcare is a fact. Thanks to LMM models, medical facilities can finally offer service that is both infinitely scalable and highly personal. This is technology that not only optimizes costs but, above all, restores dignity and peace of mind to patients during the registration process.
Would you like to see how an “empathetic” voice assistant can transform the work of your registration desk? Our advisors will present a demo based on the latest LMM models. Contact EasyCall and step into the highest standard of patient service today.
FAQ – The Empathy Revolution and LMM Models in Healthcare
Does the patient always know they are speaking with artificial intelligence?
In accordance with AI ethics and new legal regulations, the patient should be informed at the beginning of the conversation that they are being assisted by a voice assistant. However, thanks to LMM models, this information no longer causes resistance, as the quality of the conversation does not differ from human standards.
How does an LMM system handle seniors who speak more slowly or take long pauses?
This is one of the greatest advantages of the new technology. LMM models are resistant to so-called “silence on the line.” The system patiently waits for the completion of a thought, does not interrupt, and can extract meaning from speech that is not perfectly grammatically structured.
Can an empathetic bot replace a conversation with a nurse or a doctor?
No—and that is not the goal. The bot’s task is to relieve staff of bureaucratic and logistical burdens (registrations, cancellations, information about preparation for tests). This allows medical personnel to have more time for real, human empathy during the visit in the office.
What happens if an LMM bot detects very strong fear or aggression in a patient?
Systems are equipped with sentiment analysis modules. In critical situations, when voice parameters indicate severe stress or a life-threatening scenario, the bot can immediately switch the call to a priority line with a consultant or suggest contacting an emergency number.
Is implementing LMM models more expensive than traditional voicebots?
The investment in Voicebot 2.0 (LMM) technology pays back faster due to higher effectiveness (the so-called success rate). Fewer calls end unsuccessfully or require transfer to a human, which optimizes the facility’s operational costs.
Can LMM models “hallucinate” (provide false medical information)?
At EasyCall, we use a Grounded AI approach. This means the bot draws knowledge exclusively from the authorized knowledge base of your facility. If a patient asks about something outside its scope (e.g., a medical diagnosis that the bot is not permitted to make), the system will politely refer them to a physician.
How long does it take to implement an “empathetic” bot in a large clinic?
Thanks to ready-made language models, implementation is surprisingly fast. Most of the time is spent on integration with the HIS system and adapting the knowledge base to the clinic’s specifics, which typically takes between 4 and 8 weeks.
How can you check whether patients are satisfied with conversations with the new assistant?
The system automatically generates satisfaction reports. After the conversation ends, the bot may ask, “Did I help you resolve your issue today?” Statistics show that with LMM models, the rate of positive responses increases by approximately 30% compared to older systems.
